The Causes of Traumatic Brain Injury
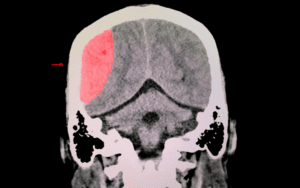 A traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs when an external force causes damage to the brain. The brain can be injured in several ways, including a blow to the head, a sudden jolt or movement that causes the brain to move rapidly within the skull, or an object that penetrates the skull and damages brain tissue.
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs when an external force causes damage to the brain. The brain can be injured in several ways, including a blow to the head, a sudden jolt or movement that causes the brain to move rapidly within the skull, or an object that penetrates the skull and damages brain tissue.
There are many different causes of traumatic brain injury, some of which include:
Falls
Falling is one of the most frequent causes of TBI, especially among older adults and children. Falls can happen due to slippery or uneven surfaces, poor lighting, or inattention.
In older adults, falls are often caused by a combination of factors, such as:
 Age-related changes in the brain and nervous system
Age-related changes in the brain and nervous system - Medications that can cause dizziness or lightheadedness
- Visual impairment
- Weakness or balance problems
- Environmental hazards, such as loose rugs or stairs
In children, falls are often caused by:
- Inexperience
- Curiosity
- Playing in dangerous areas
- Not wearing helmets when biking or skateboarding
The head may strike the ground or another object when someone falls. This may result in the brain shifting inside the skull, which can lead to bruising, bleeding, and swelling. The force of the collision and the injury site affect how severe a TBI will be.
Motor Vehicle Accidents
Car accidents, motorcycle accidents, and pedestrian accidents can all result in traumatic brain injury and are also one of the leading causes of this type of injury. The brain may slam against the skull or twist inside it due to the abrupt impact of a collision, causing damage.
Assault
Physical assault or domestic violence are examples of violent acts that can cause traumatic brain injury when someone suffers blows to the head or a sudden jolt when pushed or thrown violently.
 Sports Injuries
Sports Injuries
Contact sports that involve high-speed impact or collision, such as football, hockey, and boxing, can cause traumatic brain injury. Other sports can also be risky when there is the possibility of falling or being hit in the head with a ball or other equipment.
Penetrating injuries
Penetrating injuries, such as gunshot wounds, lead to what is called an open head injury. The penetration causes a skull fracture and damages brain tissue.
High-velocity object brain injuries are frequently accompanied by long-term effects such memory loss, decreased speech, post-traumatic epilepsy, and reduced motor abilities. The mortality rate for these high-velocity injuries is 92 percent.
Those who survive an open head injury can experience severe complications. Infections (including meningitis), dementia, convulsions, coma, and paralysis are examples of complications. Usually, an infection brought on by an open head injury will show up in the brain or its surrounding membranes. This disruption of the blood-brain protective system can interfere with the normal neural function of the brain.
Explosive Blasts
Military personnel exposed to explosive blasts are at risk for traumatic brain injury due to the blast’s force. In the case of a blast injury, the blow to the head is not from direct physical force but rather by concussive forces from the sounds or explosions. These types of injuries can occur in industrial or construction settings, such as mining. In these circumstances, explosions may cause blast injuries when concussive sound waves apply force to the brain and body harming the brain and internal organs without any direct physical contact. Shrapnel from an explosion’s aftermath has the potential to cause head injuries as well.
Hypoxia or Lack of Oxygen
Brain damage can also be the result of hypoxia or lack of oxygen. Heart attacks, respiratory failure, or an atmosphere with low oxygen levels can all contribute to this. When the brain is not receiving oxygen, it cannot function properly which can result in hallucination, confusion, and disorientation. The depletion of oxygen to the brain can cause irreversible brain damage, including the loss of memory and cognitive function.
 The severity of a TBI depends on the force of the impact and the location of the injury, and can range from mild to severe, with mild injuries often resolving on their own and severe injuries requiring medical intervention and rehabilitation. They can be temporary or permanent in nature. Regardless of the severity, it is important to seek medical attention immediately following a suspected traumatic brain injury to prevent further damage and ensure proper treatment.
The severity of a TBI depends on the force of the impact and the location of the injury, and can range from mild to severe, with mild injuries often resolving on their own and severe injuries requiring medical intervention and rehabilitation. They can be temporary or permanent in nature. Regardless of the severity, it is important to seek medical attention immediately following a suspected traumatic brain injury to prevent further damage and ensure proper treatment.
Get Help from Experienced Traumatic Brain Injury Lawyers
If you or anyone you know has suffered a severe traumatic brain injury, let the brain injury lawyers at Harding Mazzotti, LLP help today. Call our experienced legal professionals for a free consultation at 1-800-LAW-1010. We’re here for you 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
BIG RESOURCES, BIG RESULTS, BIG RELIEF. THINK BIG®
